
That being said, there are many different reasons why a website is using cookies, such as: Session managementĪ process of securely carrying your information through various sessions.

What are cookies used for?Ĭookies are used to deliver different types of information from the user’s browser to the website he is visiting. Since then, cookies have become an integral part of users’ web browsers.
The term itself is an allusion to the Fortune Cookie, a Unix application that produces different messages (or fortune) each time when they start. One tiny text file stored on a user’s computer could solve this problem. They were trying to find a way how certain websites could “remember” the customer’s personal data and items they want to buy.
BROWSER COOKIE VIEWER HOW TO
The “term” cookie was first created in 1994 by the Netscape team of developers who were trying to figure out how to solve the problem of online shopping. Cookies are very common, and you probably have thousands of them stored right now on your computer. It enables the websites to work more efficiently, recognizing and remembering certain information, such as login details. This file is sent from a website to the person’s browser where they get saved before going back to the same website.Įach cookie is unique in its own way and can’t pass viruses or capture personal information on your computer. Why do I see alerts about the use of cookies on some websites?Ĭookies (also known as internet cookies, web cookies, browser cookies, or HTTP cookies) are small pieces of information in the form of a text file, containing a string of letters and numbers.To delete a cookie, select it and click Delete selected in the top action bar. To filter out valid cookies, check Only show cookies with an issue in the top action bar. # Edit a cookieĪll the fields are editable except Size that updates automatically.ĭevTools highlights cookies with invalid field values in red. Enter a Name and Value and press Enter.ĭevTools populates other required fields automatically.
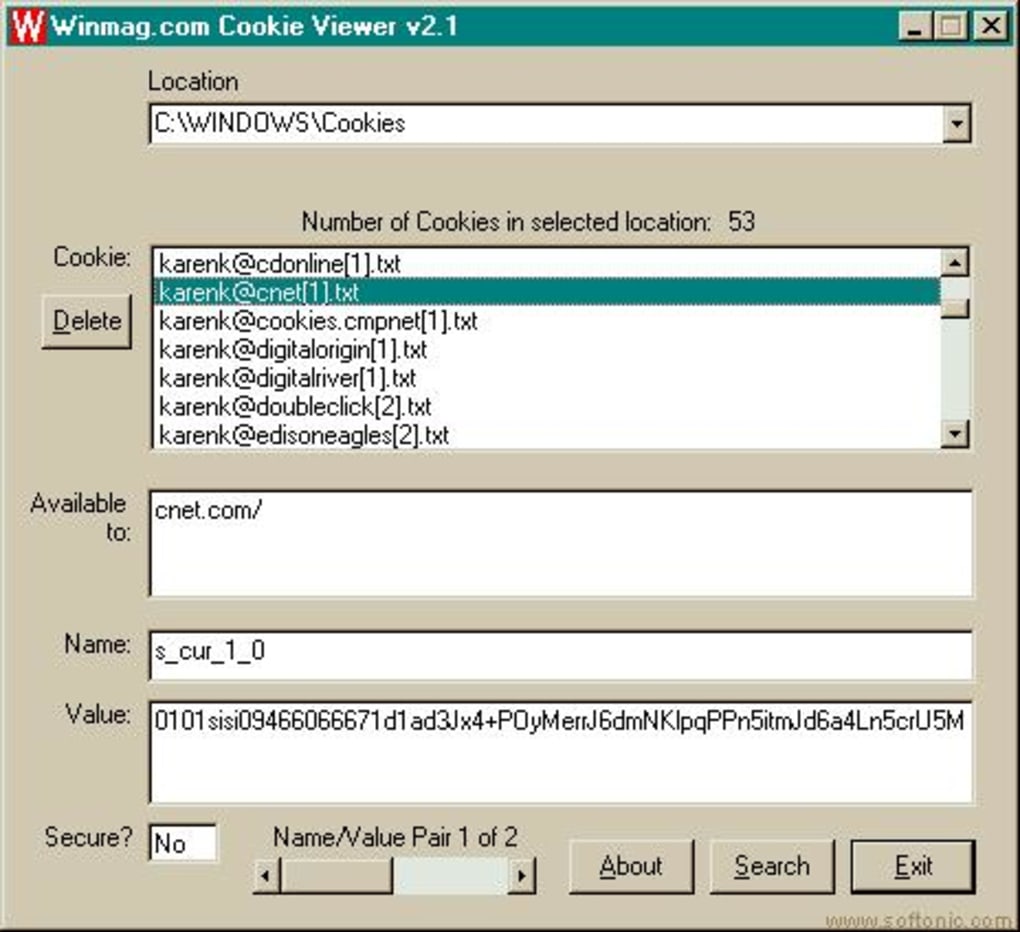
Double-click an empty row in the table.Use the Filter text box to filter cookies by Name or Value.įiltering by other fields is not supported. To see the value without percent-encoding, check Show URL-decoded. To view a cookie's value, select it in the table. Contains Low, Medium (default), or High if using deprecated cookie Priority attribute. For cookies with independent partition state, the partition key is the site of the top-level URL the browser was visiting at the start of the request to the endpoint that set the cookie. Contains Strict or Lax if the cookie is using the experimental SameSite attribute. If true, this field indicates that the cookie can only be sent to the server over a secure, HTTPS connection. If true, this field indicates that the cookie should only be used over HTTP, and JavaScript modification is not allowed. For session cookies this value is always Session. The cookie's expiration date or maximum age. The URL that must exist in the requested URL in order to send the Cookie header.

The hosts that are allowed to receive the cookie. The Cookies table contains the following fields:


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
